Medication Error is Common and Life-threatening
|
|
|
 Prescription
|
 2 in 5
|
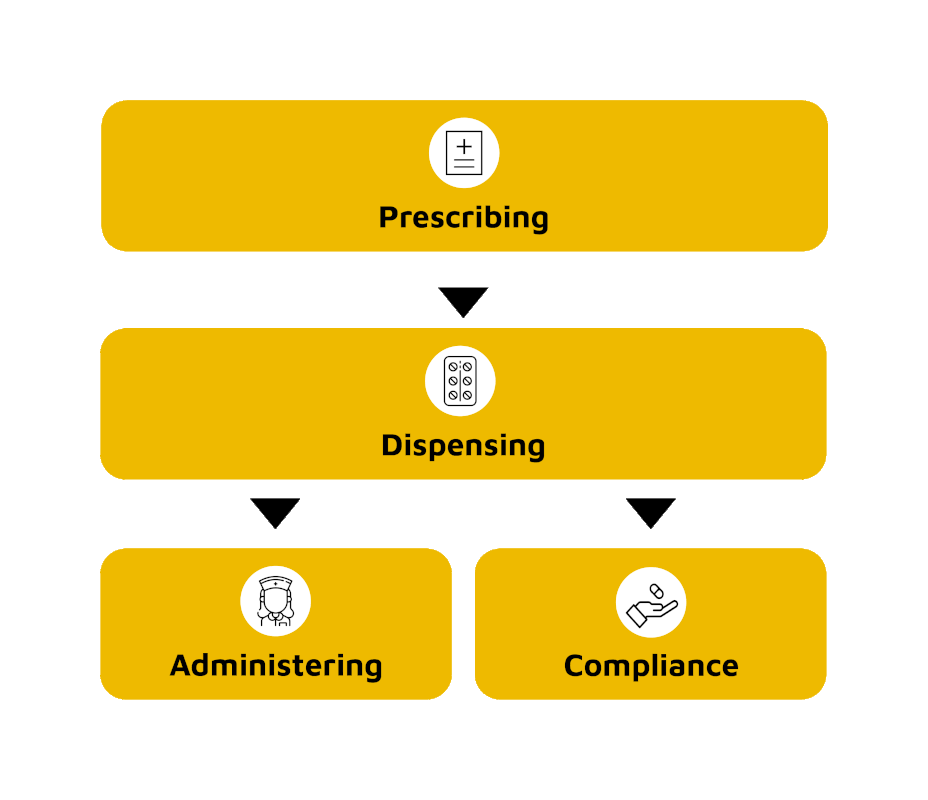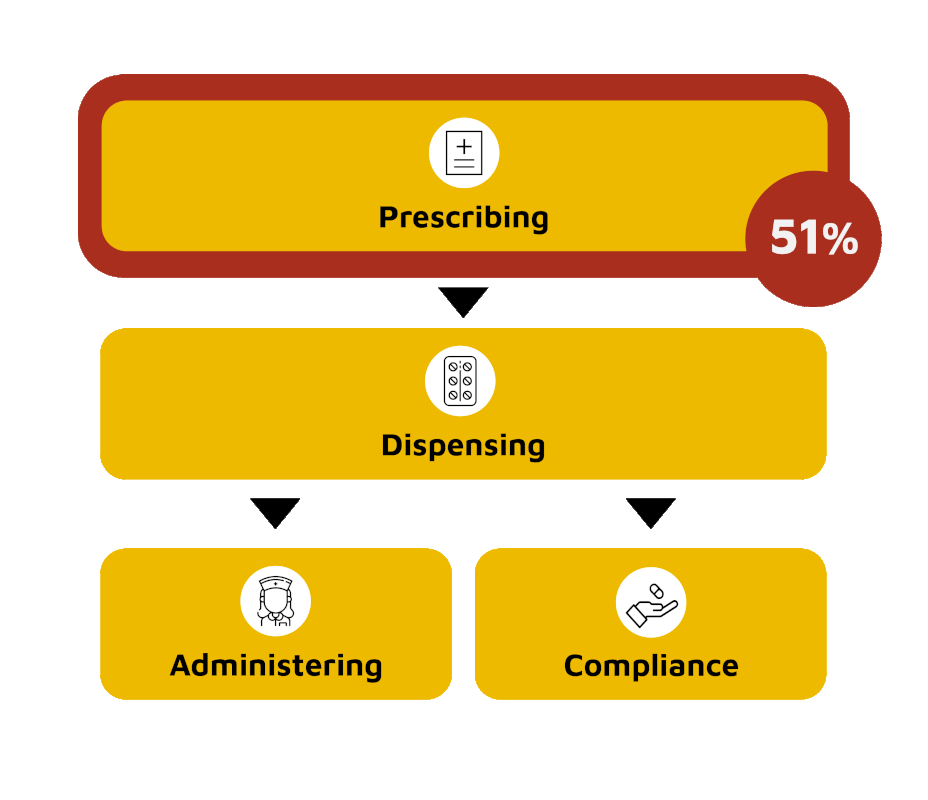
A right start is half the battle wonMedication errors can happen at any stage of the medication-use process and have severe consequences for patients. However, these errors are preventable. More than half of medication errors occur during the prescribing phase, which involves writing and issuing medication prescriptions. RxPrime helps to identify and prevent errors during this phase, including look-alike-sound-alike errors, which occur when two or more medications have similar names or sounds and can lead to confusion. By utilizing RxPrime at the beginning of the prescribing process, healthcare providers can ensure that the correct medication is prescribed to the patient, improving patient safety.
|
| The Medication-Use Process |
|
Better Decision Support for Unexplained MedicationRxPrime helps to detect potential errors in prescriptions. It provides alternative recommendations based on the patient's diagnoses, age, and gender, considering multiple perspectives, including the department and hospital-wise. It offers real-time decision support without disrupting the clinical consultation process. In this way, RxPrime enhances prescriptions' accuracy and safety, reducing the risk of medication errors and improving patient outcomes. |
|
 3.2B Prescription DatabaseRxPrime is built on an extensive database of well-coded prescriptions, containing over 3.2 billion records and 2.4 billion association rules. This data is used to support medication decision-making by analyzing explicit and tacit knowledge and clinical behaviors from doctors. Essentially, RxPrime can use this data to identify patterns and trends in prescription practices, which can then be used to support more informed and accurate prescribing decisions. |

Dual AI EngineRxPrime is powered by a dual artificial intelligence engine with customized algorithms designed specifically for medication safety. These algorithms allow RxPrime to self-improve continuously and reduce alert fatigue, providing better support to healthcare providers. Using artificial intelligence, RxPrime can analyze large amounts of data and identify patterns and trends that may not immediately appear to humans, providing more accurate and relevant support to physicians when prescribing. |
|
|
|
U.S., Taiwan Partner to Improve Patient SafetyAccording to our clinical study conducted in partnership with Harvard Medical School and Taipei Medical University, RxPrime's alert accuracy ranged from 79%-85%. This study used the international federated learning approach, which is a method of training machine learning models on decentralized data, ensuring the transferability of the results. The result showed that RxPrime effectively identifies potential prescription errors and provides accurate recommendations when applied in different countries. |

Rapid DeploymentRxPrime uses modern software engineering methods to provide high flexibility and integration options. It is designed to be easy to deploy and use, with a range of options available depending on the healthcare organization's needs. One way to deploy RxPrime is by hooking into APIs, which allows it to be integrated into a hospital's existing systems and processes. Alternatively, it can be deployed using a plugin installation on individual workstations, which is a quick and easy way to support small-scale rollouts or large-scale implementation. This flexibility makes RxPrime a suitable solution for a wide range of healthcare organizations, regardless of size or IT infrastructure. |

Satisfaction GuaranteeRAESOP is committed to helping our customers deliver high-value healthcare by providing tools and services like RxPrime. We are confident in the quality and effectiveness of its products. As such, we offer a strong satisfaction guarantee that it is among the best in the clinical decision support system (CDSS) industry. If you are unsatisfied with RxPrime, you can cancel your subscription anytime. |
|
|
|
|
|
In the light of increasing complexity of healthcare and the aging population, there is a very clear trend that there are more medical errors happening every day. Tools that our offer by companies like AESOP provide us a way to tackle this serious worldwide problem with innovative AI tools. We are very hopeful that in the future AI is going to help us reduce error and improve patient safety significantly.

Dr. Yu-Chuan Jack Li
Distinguished Professor College of Medical Science and Technology Taipei Medical University Chief & Dermatologist Taipei Municipal Wanfang Hospital President International Medical Informatics Association |
|
|
We’re living in an exciting time. We now have more data because of the EHRs that we’ve installed across the country in the world. Yet we’ve not built tools that allow us to harvest that data. AI and machine learning provide new opportunities to improve medication safety. Approaches like AESOP will allow us to understand multiple drug interactions as well as age and drug interactions, and diagnosis and age interactions, so that we can improve medication safety for all of our citizens.

Prof. Charles Safran
Chief Harvard Medical School Division of Clinical Informatics Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center |

Request More
|
|